Orchidectomy Procedure: Types and Recovery

Treatment Duration
30 Minutes
------ To ------40 Minutes
Treatment Cost
₹ 21,000
------ To ------₹ 1,10,000

Table of Contents
- What is Orchidectomy?
- Why Is Orchidectomy Done?
- What Will Happen if Orchidectomy Surgery Is Delayed?
- How is Orchidectomy Performed?
- What to Expect Before Orchidectomy?
- What to Expect During Orchidectomy?
- What to Expect After Orchidectomy?
- What is Recovery and Post Op. Care after Orchidectomy?
- What are the Risks and Complications of Orchidectomy?
You can check Orchidectomy Cost here.
What is Orchidectomy?
An orchidectomy is an operation to remove one or both of your testicles. Testicles are two small organs located in a skin sac under your penis.
Expert Doctors (10)
NABH Accredited Hospitals (10)


Why Is Orchidectomy Done?
An orchidectomy is a surgical procedure where the urologist removes one or both of your testicles. Your urologist may suggest orchidectomy in one of the following conditions:
- Prostate cancer, testicular cancer, or male breast cancer.
- If your testicles are damaged due to an accident or sports injury.
- As a part of your transition process from male to female. This surgery will help to reduce the male hormone to a great extent.
- If you are transgender, orchidectomy is preferred over long-term hormonal therapy to lower your male hormone levels.
Orchidectomy for testicular cancer:
- Testicular cancer is a rare cancer. However, it is the most common kind of cancer in young men. This cancer can be easily managed if detected early. To diagnose testicular cancer, you will undergo an ultrasound scan of your scrotum. An ultrasound scan helps the urologist understand the type, grade, and stage of testicular cancer.
- If a lump is present in your testicular region, your urologist will suggest an orchidectomy rather than a biopsy (a procedure in which a small amount of mass is removed for laboratory tests). This is because biopsy can cause cancer cells to spread.
- The pathologist will look at the surgically removed mass to determine if there is cancer, the type of cancer and how aggressive the cancer is.
- If you feel or see any of the changes listed below in your testicles, prostate, or chest area, you should visit your general practitioner. These could be symptoms of testicular, prostate, or male breast cancer.
Symptoms of testicular cancer include:
- Painless lump or swelling in one of your testicles
- Change in shape and texture of your testicles
- Feeling of heaviness in your scrotum
- Dull or sharp pain in your scrotum or testicles
- A difference in the appearance of both the testicles.
Symptoms of prostate cancer include:
- Frequent urge to urinate, especially at night
- Difficulty to start urinating
- A need to strain while passing urine
- Weak urine flow
- Blood in your urine
- Feeling that you have not passed urine completely.
Symptoms of male breast cancer include:
- A hard and painless lump in your breast
- Hard or swollen nipples
- An unhealed sore or rash in the area around your nipples
- Fluid coming out of nipples which may also contain blood
- Inward turning of the nipple
- Lumps in your underarm.
It is not necessary that the swelling or other symptoms are due to cancer. For example, you might just have swollen blood vessels. But it is better not to ignore it and get yourself checked to rule out all the causes. Also, if you are diagnosed with cancer at an early stage, its treatment will be more effective.
What Will Happen if Orchidectomy Surgery Is Delayed?
Delaying surgery during cancer:
If you have any of the cancers mentioned earlier, it is advisable to undergo orchidectomy as soon as possible. Delaying surgery can cause the following complications:
- Cancer can spread from its original location to different parts of your body.
- Your chances of survival can reduce.
- If you have cancer, it can be managed effectively using different treatment options. But the earlier you undergo surgery, the lesser the chances of spread of cancer.
Delaying surgery after an accident or injury:
If you delay orchidectomy after an accident or injury, it may lead to the following complications:
- Fluid or pus build up inside your scrotum
- Infertility
- Shrinking of the testicles.
Delaying surgery for transition process:
Apart from a delay in your transition process, orchidectomy will not cause serious problems.
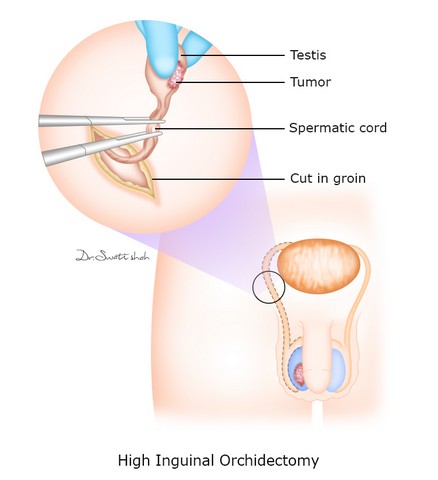
How is Orchidectomy Performed?
You will be placed in a supine position (a position in which you are lying down horizontally with your face up). Your urologist will perform orchidectomy in the following steps:
- Your urologist will first clean the site of surgery and mark the testicle which needs to be removed.
- Then, they will make a five to 10 cm incision (cut) either in your pubic area or scrotum.
- Based on the reason for orchidectomy, your urologist may remove one or both the testicles. They will also remove the blood vessels and tubes attached to the testicles.
- After the incision, the urologist will push up the testicle from your scrotum. They will not remove your scrotum or penis during the surgery.
- You will also have a choice to place a prosthetic testicle inside your scrotum. A prosthetic testicle is implanted in place of the surgically removed testicle. It is made of soft plastic and is filled with a salt-water mixture. This helps your testes to have a natural appearance after the surgery.
- After the urologist removes your testicle and places a prosthetic testicle, they will stitch the incision.
- Usually, orchidectomy requires 30 minutes to one hour.
- Orchidectomy is an outpatient procedure. An outpatient procedure means that you do not need to stay overnight in the hospital after surgery.
Orchidectomy can be of three types:
- Unilateral orchidectomy: In this surgery, your urologist will remove only one testicle.
- Bilateral orchidectomy: In this surgery, your urologist will remove both testicles.
- Radical inguinal orchidectomy: In this surgery, along with the testicles, your urologist will also remove the spermatic cord, which carries semen (a fluid that carries sperms) from your testes to the penis.
What to Expect Before Orchidectomy?
Before undergoing orchidectomy, you will have an appointment scheduled with your urologist. You will have the following discussion during the appointment:
- They will also discuss the procedure and risks of orchidectomy. At this point, you can also ask questions related to the surgery.
- If you are taking medicines that cause blood thinning, your urologist will advise you to stop using them before surgery.
- Your urologist will also suggest you a prosthetic testicle in place of the surgically removed testicle.
Your urologist will suggest the following laboratory tests before the surgery:
- A blood test to identify tumour markers like alpha-fetoprotein, beta-human chorionic gonadotropin, and lactate dehydrogenase. By observing tumour marker levels, your urologist will understand how much cancer has spread into your body.
- A sperm check-up to check your sperm count. If your healthy sperm count is low, your urologist will recommend freezing your sperm before surgery. Freezing your sperms will help you to father a child in future.
- A computed tomography (CT) scan of your pelvis, chest, and abdomen. By viewing the results of your CT scan, your urologist will understand if the cancer has spread to other parts. Before undergoing a CT scan, you should inform your doctor if you have a health condition like asthma or if you are allergic to iodine.
If your urologist allows you to consume your routine medicines before surgery, take them with only a sip of water.
What to Expect During Orchidectomy?
On the day of surgery, after reaching the hospital, you will meet the healthcare staff, who will guide you through the process before the surgery.
Anaesthesia:
For undergoing orchidectomy, you will be administered general anaesthesia.
Position and draping for surgery:
- When you are in the operating room, the healthcare staff will place you in a supine position.
- Your body between the nipple line and mid-thighs will be cleaned with an antiseptic solution.
What to Expect After Orchidectomy?
At the hospital:
- When you wake up, you will notice that you have a dressing at the site of surgery. The healthcare staff will remove this dressing one day after your surgery.
- Before discharge, the healthcare staff will perform specific tests, and the urologist will discuss the reports during the follow-up.
- Once you are discharged, you will need your family member or friend to drive you home.
Medications:
During orchidectomy, the urologist removes your testicles which can cause your male hormones to drop. Because of this, you may experience side effects like depression, tiredness, hot flashes, low muscle mass, and sexual dysfunction. To relieve these side effects, your urologist may prescribe you hormonal supplements.
Diet:
- After surgery, the healthcare staff will advise you to consume clear liquids. This is because anaesthesia can make you feel nauseous, and you may also have other stomach discomforts.
- Based on how your body tolerates regular food, you can start to consume such foods.
- Once you are discharged, eat fibre-rich foods, and stay hydrated to prevent constipation.
What is Recovery and Post Op. Care after Orchidectomy?
Recovery:
- For the first few days after orchidectomy, your surgeon will recommend you do the following:
- Keep your surgical site clean and dry. You can clean the surgical area by gently patting. You should cover the surgical site by using gauze.
- If you feel pain in your scrotum, apply ice packs after every 20 minutes. You can use icepacks for one or two days post-surgery.
- Do not strain too much while passing your faeces.
- Your urologist will suggest wearing a particular garment (to support your scrotum) for two days after surgery.
- Wear loose clothes for a few days after orchidectomy. This is because your surgical site might be swollen after the operation.
- Your surgeon will advise you to follow the instructions listed below for more than a week or until your surgical site is healed:
- You should avoid strenuous activity (e.g., running) or lifting heavy objects until your surgical site is completely healed.
- You should wait for at least three to four weeks before performing physical activity or sex. This is because complete recovery takes up to four weeks post-surgery.
- You can resume your daily work after one to two weeks post-surgery.
First Follow up Appointment
- Your urologist will schedule a follow-up appointment two weeks after orchidectomy. A follow-up is scheduled after two weeks because it takes about two weeks for the pathologist to check your blood samples and the surgically removed testicle and generate the results.
- During the follow-up, your urologist will review the reports, check how well you are doing, and schedule any blood tests, if necessary.
- If cancer is detected via laboratory tests, an oncologist (a doctor for cancer) will also join the appointment to discuss the further treatment plan.
What are the Risks and Complications of Orchidectomy?
The complications that can occur after surgery will depend on the type of surgery and whether your urologist removed one or both of your testicles. While undergoing orchidectomy, several complications can arise like:
- You may get an allergic reaction to the anaesthesia administered.
- The blood vessels surrounding your scrotum can accidentally get injured, which may lead to bleeding.
- The sensory nerve around your scrotal area can get damaged. If this happens, your upper thigh and the scrotal area will feel numb.
- You may get an infection or a bruise. There might be chances of fluid build-up or collection of blood in the scrotum.
You should visit your urologist if you experience any of the following symptoms after having an orchidectomy:
- Swelling of your scrotum.
- Extreme pain
- Redness or purple spot at the site of the surgery due to the collection of blood outside of the blood vessels at your surgical site.
- Blood or pus leaking from the site of surgery
- Looseness in your scrotum (scrotum bulging downwards more than usual)
- Trouble urinating
- High body temperature.
- Infection at the site of surgery.
Since orchidectomy involves the removal of testes, your fertility will be affected. You may lose sexual interest or face a hard time getting an erection. If the urologist removes only one testis, you will be able to produce sperms and testosterone. But if the urologist removes both of your testicles, you will not be able to produce sperms.
Also, removal of both the testicles can cause other long-term effects like:
- Hot flashes
- Increased breast size
- Decreased muscle mass
- Increased weight
- Weakening of bones
More Treatment options
Last Updated on: 13 October 2025
Author
HexaHealth Care Team
HexaHealth Care Team brings you medical content covering many important conditions, procedures falling under different medical specialities. The content published is thoroughly reviewed by our panel of qualified doctors for its accuracy and relevance.
Latest Health Articles
























