Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act, 1971

Quick Summary
- The MTP Act was amended in 2021 by the passage of the MTP Amendment Act 2021.
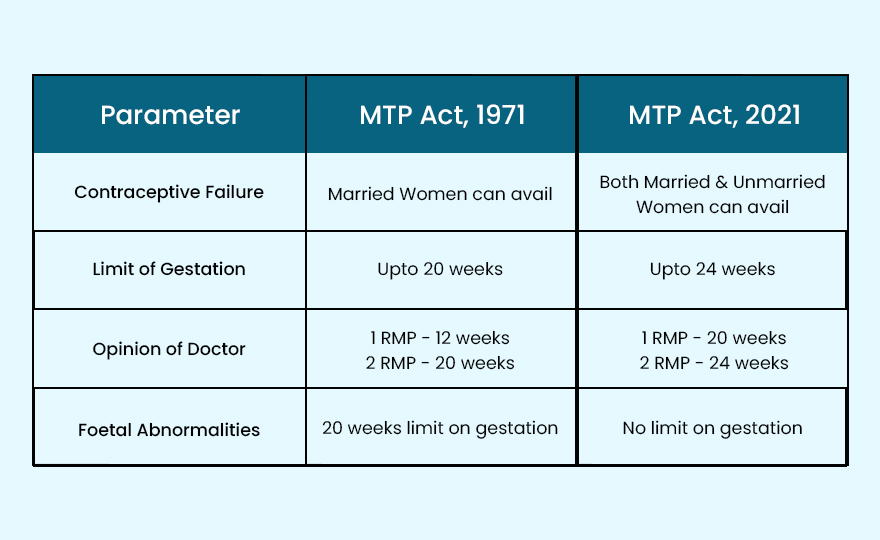
- The MTP Amendment Act 2021 allowed all women to obtain safe abortion services on the grounds of contraceptive failure.
- The MTP Amendment Act 2021 increased the gestational limit for specific categories of women to 24 weeks.
An act on abortion was permitted in India under various conditions under MTP Act, 1971. The MTP Act was amended in 2021 by the passage of the MTP Amendment Act 2021, which allowed all women to obtain safe abortion services on the grounds of contraceptive failure, increased the gestational limit for specific categories of women to 24 weeks, and required up to 20 weeks of gestation for a provider's opinion.
As per law, the term abortion refers to the premature termination of pregnancy before the full growth of the foetus. Today, abortion is a widely accepted practice across various countries in the world. However, earlier, abortion was considered an illegal practice in India for a very long time. Several women died trying to terminate the pregnancy either in an illegal way or with unhygienic methods. Read on to learn more about the termination of pregnancy under the MTP Act, 1971 and its amendments.
The Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act, 1971
 According to the legislation, an abortion is the early termination of a pregnancy before the foetus has reached its full size. Abortion is now a practise that is widely accepted in many nations throughout the world. However, for a very long period, abortion was regarded as an unlawful practise in India. Several women lost their lives while attempting to end their pregnancies, either through unlawful means or inhumane means. Anyone who tried premature termination of pregnancy with illegal methods was subjected to a punishment of imprisonment and a fine.
According to the legislation, an abortion is the early termination of a pregnancy before the foetus has reached its full size. Abortion is now a practise that is widely accepted in many nations throughout the world. However, for a very long period, abortion was regarded as an unlawful practise in India. Several women lost their lives while attempting to end their pregnancies, either through unlawful means or inhumane means. Anyone who tried premature termination of pregnancy with illegal methods was subjected to a punishment of imprisonment and a fine.
Due to these reasons, the legislature of India realised that making abortion illegal was negatively affecting women’s health with unwanted pregnancies. As a result, a Medical Termination Bill was proposed in the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha in 1969 and passed by the parliament in 1971. With this law, known as “The MTP Act, 1971,” the termination of pregnancies was legalised. However, it did not apply to all types of pregnancies.
Before 1971, abortion was considered illegal in India. However, there were certain provisions related to abortion in Section 312 to Section 318 of the Indian Penal Code, 1860.
- Section 312 and 313 cover the offence of causing miscarriage.
- Section 314 deals with the death of women during a miscarriage.
- Section 315 and 316 are related to injury caused to the unborn child.
- Section 317 deals with the abandonment and exposure of an infant.
- Section 318 deals with the concealment of the birth of a child.
As per the MTP Act, 1971, a woman can get her pregnancy terminated only in Government-approved hospitals by a registered medical practitioner. Section 3 of the MTP Act, 1971 laid down some conditions under which a pregnancy can be terminated. These conditions include:
- The pregnancy arises from crimes such as sexual assault or rape.
- It causes a risk or danger to the woman’s physical or mental health.
- The child has a risk of being born with a physical or mental malformation.
- Girls under 18 who are insane or lunatic cannot get their pregnancy terminated without the written consent of a parent or guardian.
- Abortion is allowed till the 20th week of pregnancy.
- Abortion up to 12 weeks of pregnancy requires the opinion of one registered medical practitioner.
- Abortion between 12 to 20 weeks requires the opinion of two registered medical practitioners.
Under the MTP Act, 1971, only married women and rape victims were allowed to terminate their pregnancies. Unmarried women, divorced women, or widows were deprived of this right, due to which they either continued their pregnancies or opted for illegal methods of abortion.
Book Consultation
Shortcomings of the MTP Act 1971
The law was criticised due to its several shortcomings, which include:
- Several tests are performed in the 20th week of pregnancy to detect abnormalities that are only confirmed after the 20th week. However, the act did not allow the termination of pregnancy beyond 20 weeks.
- It failed its basic objective of offering safety and empowerment to pregnant women by restricting them from terminating the pregnancy of their free will.
- It was introduced in 1971 when technology was not highly evolved. Hence, there was a need for new provisions as per the evolutions in technology.
- It increased the complexity of legal procedures.
- Even married women had to prove contraceptives’ failure to terminate their pregnancy, violating the fundamental right to privacy.
Due to these shortcomings, the Medical Termination of Pregnancy (Amendment) Act 2002 was introduced.
The Medical Termination of Pregnancy (Amendment) Act, 2002
The following provisions were taken into account in the Amendment Act:
- A committee operated at the district level was responsible for deciding whether private establishments could provide abortion services.
- One needed to strictly comply with the provisions of time and location for pregnancy termination under the act. Otherwise, harsh penalties were implemented.
- For psychological illnesses, the term ‘lunatic’ was substituted with ‘mentally ill person.’
The MTP Act 2002 bought some changes. However, several amendments were still to be made that were introduced in the form of the Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act, 2021.
The Medical Termination of Pregnancy (Amendment) Act, 2021
 With the advent of technology in the healthcare sector, there was a need for better laws regarding abortion. Thus came the Medical Termination of Pregnancy (Amendment) Act, 2021. The act addresses several issues, ranging from the right to privacy to female foeticide. It aims to decrease the preventable maternal mortality rate by broadening the applicability of the MTP Act 1971. The salient features of the Amendment Act 2021 include:
With the advent of technology in the healthcare sector, there was a need for better laws regarding abortion. Thus came the Medical Termination of Pregnancy (Amendment) Act, 2021. The act addresses several issues, ranging from the right to privacy to female foeticide. It aims to decrease the preventable maternal mortality rate by broadening the applicability of the MTP Act 1971. The salient features of the Amendment Act 2021 include:
- The act has increased the gestation period for termination of pregnancy from 20 weeks to 24 weeks for special categories of women, including rape and incest victims, physically disabled women, minors, widows, and other vulnerable women.
- Abortion up to 20 weeks of gestation requires the opinion of one registered medical practitioner.
- Abortion from 20-24 weeks of gestation requires the opinions of two registered medical practitioners.
- The act protects the privacy and confidentiality of women who opt for termination of pregnancy.
- It allows unmarried women to access safe abortion for pregnancies due to contraceptive failure.
Shortcomings of the MTP Act 2021
Like the previous acts for pregnancy termination, the MTP Act 2021 also has certain shortcomings, which include:
- The act offers different opinions on termination. While one opinion considers abortion as the choice of the pregnant woman and a part of her reproductive rights, the other links abortion to state-sanctioned conditions, protecting the foetus rather than the woman’s life.
- It allows abortion after 24 weeks only for special categories of women. Other women will still face legal ramifications for wanting an abortion after 24 weeks.
- Abortion can be performed only by doctors specialising in gynaecology or obstetrics. Due to the shortage of these doctors in rural areas, women may lack access to safe abortions.
Takeaway
The Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act 2021 offers provisions for safe and legal abortions for unplanned pregnancies. It is commendable how the Government has balanced the laws for legal abortion with the country’s societal belief system and cultural diversity. However, the Government still needs to do much more to end the practice of illegal abortions.
Have queries regarding abortion? You can consult an HexaHealth expert to talk about safe abortion practices. From consultation to finding the right hospital, we can help you avail termination of pregnancy as per the abortion laws in the country.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is abortion permitted in India?
Yes, abortion is permitted up to 20 weeks of pregnancy in India. You may do so based on the following criteria:
- When your doctor declares that carrying the pregnancy to term poses a risk to your life and could seriously harm your physical or mental health.
- When your doctors note that there is a significant chance that the child would be severely disabled and might have physical or mental problems if they were to be born
- When you assert that the failure of birth control methods is the reason for your pregnancy
- When rape or incest is the cause of your pregnancy. (In this country, the window for an abortion can be extended to 24 weeks with the consent of two registered medical practioners.)
What is the MTP Act, 1971?
According to the MTP Act of 1971, a woman may only have her pregnancy terminated by a licenced physician in a hospital that has been sanctioned by the government. The MTP Act of 1971's Section 3 set forth a few circumstances in which a pregnancy may be terminated. Only married women and rape victims were permitted to end their pregnancies under the MTP Act of 1971. Because they were denied this option, single women, divorcees, and widows either carried on with their pregnancies or chose illegal abortion procedures.
What is the MTP Act, 2021?
Better abortion legislation was required with the development of technology in the healthcare industry. The Medical Termination of Pregnancy (Amendment) Act, 2021, was born as a result. The legislation covers a wide range of topics, including the right to privacy and female foeticide. By extending the scope of the MTP Act's 1971 applicability, it seeks to reduce the rate of preventable maternal mortality.
Who is eligible to get safe abortion services under the Amendment Act of 2021?
Contrary to the original Act, which only allowed married women to use pregnancy termination as a last resort in the event that contraceptive methods or devices failed, the amendment consents to allow pregnancy termination to "unmarried women" as well, i.e., regardless of their marital status.
When are women and couples eligible to get pregnant terminated?
For foetal malformations determined by the Medical Boards, women or couples may choose to end a pregnancy at any stage throughout the gestation period.
Does choosing to end a pregnancy up to 24 weeks provide any special circumstances?
Pregnant women, women with disabilities, minors, and victims who claim that their pregnancy was caused by rape, sexual abuse, or incest may request termination up to twenty-four weeks after conception with the advice of a certified medical practitioner. With the approval of the Medical Board, a specific exception permits no maximum gestational age in cases of foetal impairment. For the termination of pregnancies up to twenty to twenty-four weeks, two qualified medical practitioners' views are also basically required.
Who is ultimately in charge of making the choice to end a pregnancy?
The revised abortion rules continue to be based more on medical advice than on a woman's preference for ending her pregnancy. Women no longer have full discretion over their reproductive options.
On "moral grounds," can a woman be denied an abortion?
It is indisputable that the idea and practise of pregnancy termination are morally questionable. But because abortion is stigmatised, even the medical profession forbids procedures when pregnant women are asked to bring their partners or parents for acceptance and procedural compliance.
What legal documentations are needed for a medical abortion?
The clinic mostly requires the following two documentations for medical abortions:
- Proof of age (18+)
- The patient's signed consent
What are the Indian legal justifications for medical abortion?
The four most common justifications for abortion in India are as follows:
- Ineffective contraception (birth control)
- Mother's bodily or mental health is seriously at stake.
- Genetic abnormalities of the foetus
- Rape, sexual assault (allowed until 24 weeks pregnancy)
What are the restrictions on the MTP Act's application based on gender?
Due to the MTP Act's specific reference to "women," including transgender people, genderqueer people, and people who identify as gender non-conforming, abortion services are not available to them.
What are the MTP Act's offences and punishments for unlicensed medical practitioners?
Pregnancy termination by a person who is not a licenced medical professional is a crime punished by strict imprisonment for a time that must not be less than two years but may reach seven years.
Where would the pregnancy be terminated in accordance with MTP Act regulations?
No pregnancy may be terminated in conformity with this Act anywhere other than (a) a hospital created or maintained by the government, or (b) a location currently approved by the government or a District Level Committee for the purposes of this Act.
Is my husband's approval required for an abortion?
No, according to the MTP Act 1971, Indian law considers conception, pregnancy, and abortion to be the woman's sole, inalienable right. This is why it is against the law for a doctor to request your husband's permission if you are over 18, are within the pregnancy's maximum gestation, and are otherwise healthy enough to have an abortion.
Last Updated on: 29 September 2023
Reviewer

A specialist in Obstetrics and Gynaecology with a rich experience of over 21 years is currently working in HealthFort Clinic. She has expertise in Hymenoplasty, Vaginoplasty, Vaginal Tightening, Labiaplasty, MTP (Medical Termination...View More
Author

Charu Shrivastava
BSc. Biotechnology I MDU and MSc in Medical Biochemistry (HIMSR, Jamia Hamdard)
2 Years Experience
Skilled in SEO and passionate about creating informative and engaging medical content. Her proofreading and content writing for medical websites is impressive. She creates informative and engaging content that educ...View More
Expert Doctors (10)
NABH Accredited Hospitals (7)
Book Consultation
Latest Health Articles
Related Treatments




























